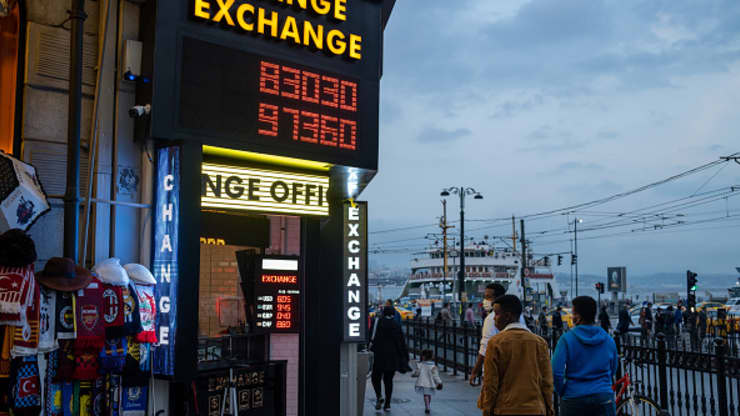President Recep Tayyip Erdogan subtly acknowledged the depth of Turkey’s financial woes in a speech to the ruling Justice and Development Party’s (AKP) annual congress last week in the Turkish capital Ankara.
“Now it is time to work harder, produce more, speed up,” he told AKP delegates. “I want my citizens to invest foreign currency and gold kept at home, which is our national wealth, in various financial instruments to benefit our economy.”
This was no idle request. A few days prior, Mr Erdogan had for the third time in 20 months fired his central bank chief. The dismissal of Naci Agbal, who had raised interest rates two days earlier, in an effort to curb persistently high inflation, shocked analysts and investors who had seen his four-month tenure as restoring credibility.
He was replaced by Sahap Kavcioglu, a pro-government columnist and former banker and AKP parliamentarian, who is said to share Mr Erdogan’s unorthodox view on inflation and interest rates. When markets opened Monday the Turkish lira quickly lost 15 per cent of its value, falling near record lows against the US dollar before regaining some ground.
Turkey’s main stock market erased its gains for the year and recorded its worst two-day stretch since the 2008 financial crisis. The Economist called Mr Agbal’s firing a “debacle”, while prominent Turkish economist Mustafa Sonmez wondered if Mr Erdogan had committed economic suicide.

Since a mid-2018 currency crisis, the lira has lost nearly half its value against the dollar and Turks have become increasingly reluctant to watch their savings evaporate. The President urged his worried countrymen to invest in Turkish instruments, highlighting the benefits of Islamic ones in particular, but many have other ideas.
Turks’ total investment in gold is equal to about 40 per cent of gross domestic product, according to Bloomberg, while dollar- and euro-denominated savings are also sizeable. Recently a fourth alternative has emerged. The cryptocurrency market remains unregulated in Turkey, with no tax laws or licensing requirements for traders.
The suicide of a young Istanbul couple, who left their baby with a neighbour, shows the extent of hardships
This, plus the falling lira and bitcoin’s five-fold leap in value in recent months, has driven sharp Turkish interest. As of early 2021, Turkey’s two main crypto exchanges, Paribu and BtcTurk, averaged more than $1 billion in daily trading.
A February survey by the German consumer research firm Statista ranked Turkey fourth globally in terms of crypto ownership, at 16 per cent of the population. A 30-year-old Turkish crypto investor says the digital currency has come to mean two things to Turkish youth: “future and freedom”.
Mr Agbal’s dismissal sped up this trend. The next day internet searches for “Bitcoin” quadrupled in Turkey, hitting Google’s highest search value. Turkey’s crypto exchanges saw a record $6 billion in trades over a 24-hour period and registrations of Turkish users on British crypto exchange CEX.IO leapt nearly 800 per cent.
Turkey’s central bank is unlikely to start regulating the crypto space anytime soon, as its plate is full trying to calm market jitters. It is too soon to predict the extent to which Turkish interest in crypto currencies might shape markets, but it could be an increasingly appealing alternative if the lira remains weak and economic despair deepens.

Last month, the joint suicide of a young Istanbul couple, who left their one-year-old child with a neighbour, highlighted how more and more Turks facing financial hardship are taking the most drastic steps. Just last week, the Turkish Musicians and Performers Union (Muzik-Sen), announced that more than 100 musicians have committed suicide since the start of the pandemic, most after losing their jobs and receiving inadequate state aid.
Turkey was one of the few countries to avoid economic contraction in 2020, and it is still some way from the desperation of Lebanon, where the economy faces total collapse, as people in Beirut wrestle over basics in grocery stores. But such scenes may be in Turkey’s future.
With Covid-19 lockdowns driving more than 1.5 million Turks into poverty, about 20 per cent of the country now lives below the poverty line. Around seven in 10 have significant debt, one in three have difficulty buying food or heating their home, and 40 per cent of people under 30 are unemployed.
Meanwhile, the pandemic’s third wave is cresting as new daily cases top 30,000, equalling Turkey’s December peak. This is likely to mean more lockdowns, and more income-free weeks for countless people as inflation and lira depreciation bite. Many observers criticised the AKP for inviting hundreds of party members from around the country to gather for days in proximity indoors, with many attendees not wearing masks at last week’s congress.
Losing popularity, the AKP has sought to rally its base by highlighting its conservatism and Islamic bona fides. For many, this explains Mr Erdogan’s recent decision to pull Turkey out of the world’s leading compact for preventing violence against women, the Istanbul Convention, which Islamists saw as challenging their views of the traditional family.

Another way the government has pushed Islam is by employing the significantly expanded Diyanet, or Directorate of Religious Affairs, to promote deprivation and resignation. The Diyanet writes the Friday sermons for Turkey’s 82,000 mosques, and in recent weeks the speeches have repeatedly praised poverty and obedience to authority.
The Diyanet has issued fatwas advising people to cut down on unnecessary purchases and go to farmers’ markets in the late afternoon to save money. Another sermon reminded Turks that “poor people are closest to God”. Last week, as markets shuddered, the chief imam of Istanbul’s iconic Hagia Sophia mosque tweeted: “God will test believers with fear and hunger, with a decline in their lives and belongings, but God will award the patient ones at the end.”
But the president is singing a different tune, arguing in his speech that the latest fluctuations do not reflect the economy’s fundamentals, and pointing to the thousands of new businesses and robust infrastructure as reasons the Turkish economy is headed for a new peak.
Towards the end of his speech Mr Erdogan unintentionally underscored his government’s failings: “The pandemic has revealed very clearly that the powerful states are not the ones that have a lot of money,” he said, “but the ones that offer the best service to their citizens in times of need.”
In a time of grave need, Mr Erdogan’s government is removing safeguards – a steady hand at the central bank, Covid-19 restrictions, the Istanbul Convention – while telling its increasingly desperate citizenry to have faith and obediently accept their fate. Apparently Turkey is not yet as powerful as its leader seems to think.
David Lepeska is a Turkish and Eastern Mediterranean affairs columnist for The National
Source: The National